The ls Command
Summary
The wget that retrieves files (downloads) from a URL through a variety of internet protocols. Those protocols include HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and FTPS. wget has a variety of options that allow the user a lot of choice when downloading files. The URL must be a direct link to the file, otherwise wget will download the .html of the site that is hosting the file.
Basic command structure
For all descriptions below, the dollar sign indicates that BASH command prompt.
$ wget [options] [URL]
Note: A URL is always required, options are not.
Possible Flags
-P
The -P flag specifies a path/directory to where the file(s) are downloaded.
-b
The -b flag downloads in the background, further commands can be inputted even if the file(s) have not been fully downloaded yet.
-i
Allows the urls to be extracted from an external file such as a .txt file, however each URL must be line-delineated.
Output
The wget command has a variety of error codes that can be outputted to a text file if used with -O. These include:
0
No problems occurred.
1 Generic error code.
2 Parse error—for instance, when parsing command-line options, the ‘.wgetrc’ or ‘.netrc’…
3 File I/O error.
4 Network failure.
5 SSL verification failure.
6 Username/password authentication failure.
7 Protocol errors.
8 Server issued an error response.
These do not include any web server errors like 404 or 403.
-
Sucessful download, correct URL with no flags, which downloads a public domain film to the current working directory:
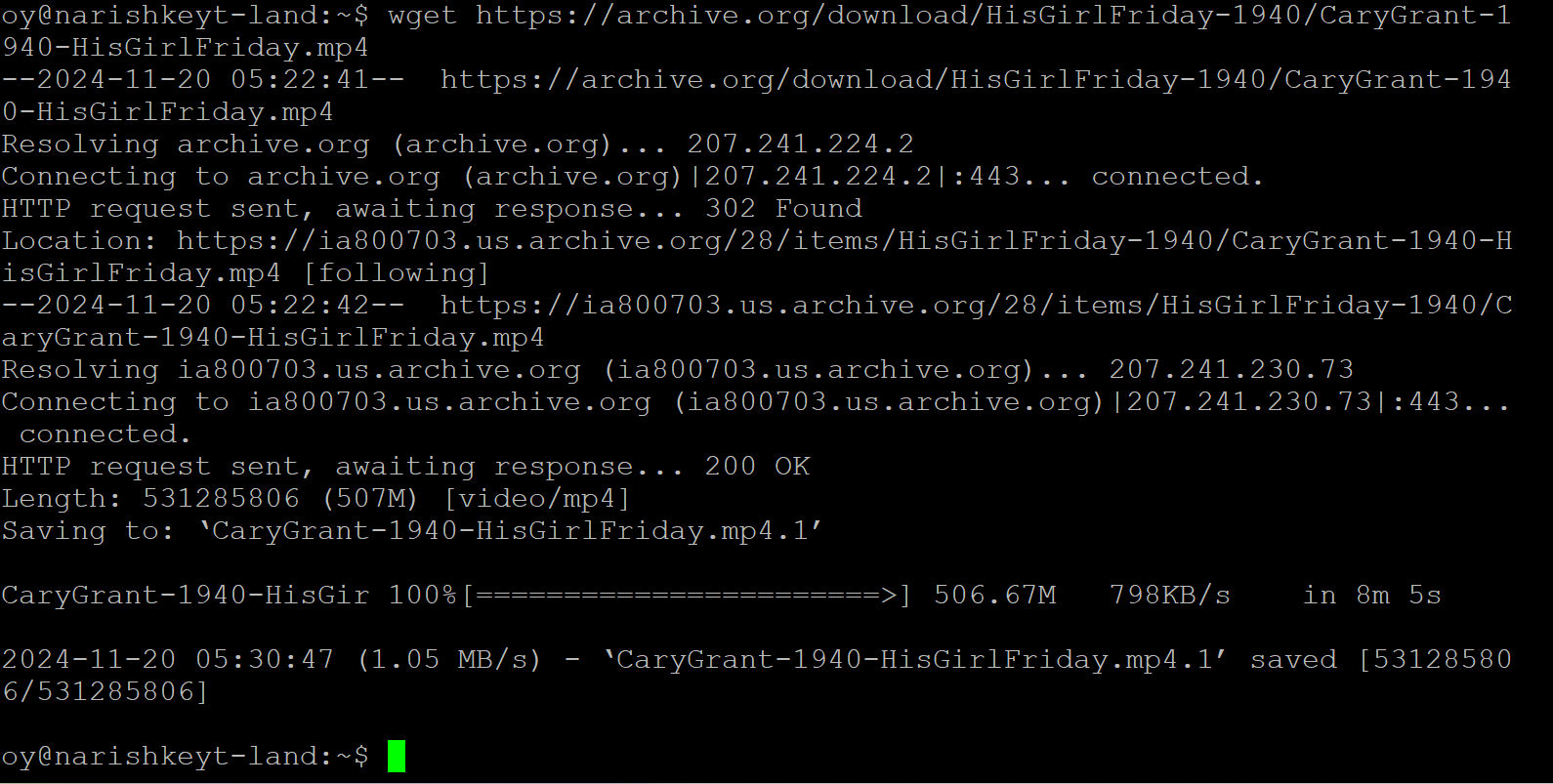
-
Unsucessful download, incorrect URL
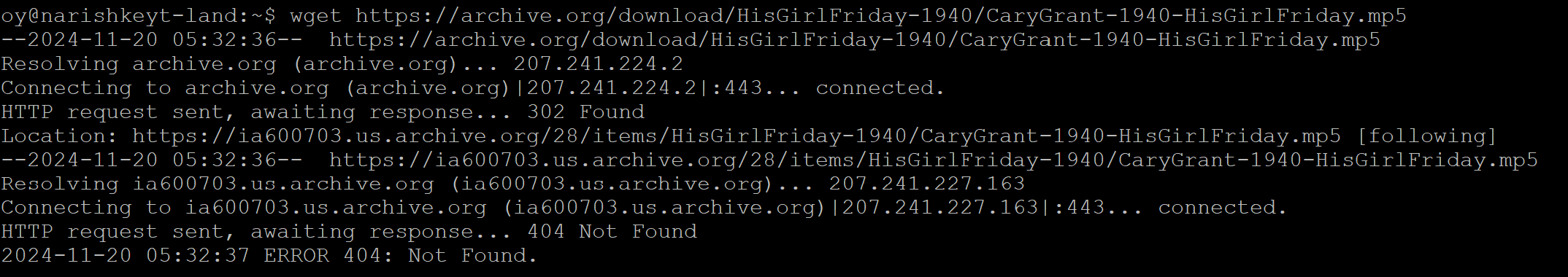
Example
- If you want to download a file in the background, use command $
wget -b ~, where~is the URL of the file without any quotation marks.
Go back to the main list of commands